 By Marek Grzybowski
By Marek Grzybowski
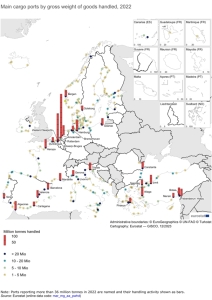
Global maritime coal trade accelerated in the last months of 2023 and returned to pre-pandemic trade levels. In the period January-December 2023, global sea coal shipments increased by 6% y/y to 1,341.2 million tons (excluding cabotage), based on ship tracking data from AXS Marine, Banchero Costa reports in the latest report. Last year global demand for steel also increased to 1.8% in 2023 to 1.814 billion tons. and in 2024 by 1.9% – we read in the February report of the World Steel Association (WSA – Worldsteel).
The situation on the European market has changed significantly since the creation of the European Coal and Steel Community. Let us recall that this organization was established on the initiative of French politicians. The originator of the idea was Planning Commissioner Jean Monnet, and the initiative was implemented by Foreign Minister Robert Schuman. The idea was to eliminate conflicts at the interface between the French and German raw materials markets. The initiative was supported by neighboring countries interested in economic cooperation.
European Coal and Steel Community
The European Coal and Steel Community was established in 1952. The duration of its operation was set in the treaty at 50 years. The treaty was signed by France and the Federal Republic of Germany, as well as Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg and Italy. Since then, the coal and steel market has transformed into the single market of the European Union.
The Saar area, the Ruhr area and Lorraine have completely changed their “mining and ore” face for over 70 years. However, coal and steel are still its important components. After years of transformation, European countries became increasingly dependent on imports of coal and steel.
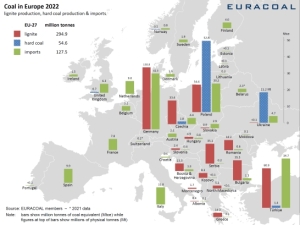
The EU accounted for 6.6% of global coal shipments by sea in 2023. Imports of coal through sea ports to the EU increased by 38.2% y/y to 127.6 million tons compared to 2022. Demand for steel in EU countries and Great Britain in 2023, according to WSA information, decreased by 5.1%. on an annual basis, and in 2024 it is expected to increase by 5.8% y/y.
– In 2023, much more coal was transhipped in bulk carrier terminals of EU seaports than in the period January-December 2022. Two years ago, transporters and cranes transported over 1,265.5 million tons between ships and quays in EU terminals. For comparison, in 2021 in 2019 it was 1,254.2 million tons, and in 2020 and 2019, 1,196.5 million tons and 1,309.8 million tons were unloaded between ships and storage yards, respectively – says Banchero Costa Research in its latest report.
The demand for sea transport of coal resulted in high activity of exporters. In the period January-December 2023, coal deliveries to the market from Indonesia via the Pacific routes increased by 10.5% y/y to 496 million tons. Mines and ports in Australia also benefited from the increase in demand. Exports from the Antipodes increased by 4.8% y/y to 344.9 million tons. From Russia, exports to the global market decreased by approximately 2.4% y/y to 184 million tons and from South Africa, coal loads decreased by 0 .3% y/y to 60.4 million tons.
Deliveries from the USA increased by 16.7% y/y
However, deliveries from the USA increased by 16.7% y/y to 86.6 million tons. Bulk carriers from Colombia delivered 2% more coal y/y to ports around the world, transporting 56.4 million tons of this black cargo in January -December 2023. Bulk carriers delivered 50.2 million tons from Canada via the Atlantic and Pacific (an increase of 10.2% y/y), and from Mozambique 23.7 million tons (an increase of 14.6% y/y).
Coal imports on sea routes were created by the People’s Republic of China, Japan, India and South Korea. Interestingly, countries with high development dynamics and innovative economies are also large consumers of coal.
Banchero Costa Research analysts found that mainland China’s bulk terminals handled 48.6% more coal in 2023 than the previous year. 368.4 million tons of this cargo were received from ships at the quays in the period January-December 2023.
Imports to Japan decreased by 10.3% y/y to 160.5 million tons in 2023, imports to South Korea decreased by 4.4% y/y to 117.4 million tons, Taiwan imported 58.3 million tons, less by 4.3% y/y. Imports to India increased by 6.9% y/y to 240.8 million tons and to Vietnam by 54.2% y/y to 47.4 million tons.
EU – coal versus natural gas and renewable energy
The European Union is currently the fifth largest importer of coal by sea in the world, after China, India, Japan and South Korea. In 2023, EU countries created 6.6% of global demand for coal imports by sea.
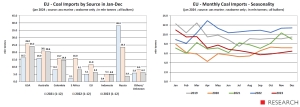
While coal imports by sea to the EU increased in 2022 by +38.2% y/y to 127.6 million tons, in 2023 imports of this energy raw material dropped sharply by 30.4% y/y to only 88.8 million tons. This is the lowest volume of coal imports in recent years after 2020, when the world was affected by the Covid-19 pandemic.
In 2023, European countries returned to demand from the previous trend, which gradually abandoned coal as an energy source. Natural gas is back in favor. Gas imports from Russia to the EU cost Western European countries approximately EUR 1 billion per month, as we wrote in GospodakraMorska.pl.
The reduction in coal imports is influenced by the dynamically growing supplies of energy from renewable sources. As a result, already in 2020 we observed a decline in European demand for coal by 32.9% year-on-year, and earlier: by 18.3% y/y in 2019, by 7.6% y/y in 2018 – Banchero enumerates Costa.
US – the most important supplier to Europe in 2023
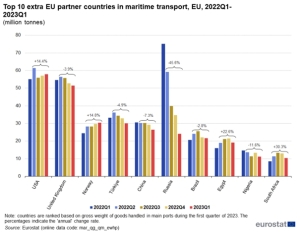
In terms of supply sources, for many years Europe, including Poland, was largely dependent on Russia. After 2022, the situation has changed dramatically. In 2021, as much as 44% of EU coal imports by sea came from Russian ports. In 2023, as a result of the sanctions imposed, this share dropped to 4.3%. This statistic also includes Kazakh coal transported through Russian ports. In the period January-December 2023, coal imports to the EU from Russian ports decreased by 83.6% y/y to only 3.9 million tons (including Kazakh coal).
The most important supplier to Europe in 2023 was the United States. EU countries from this direction met 27.3% of their needs for coal imported by sea. In 2022, deliveries of black cargo from the USA across the Atlantic to EU ports increased by 60.5% y/y to 26 million tons. In 2023, however, they decreased by 7.0% y/y to 24.2 million tons. The second largest supplier to Europe is Australia.
In 2023, 23.2% of the coal needed by the EU was imported to EU countries via the Pacific and the Suez Canal. In 2022, imports from Australia increased by 30.8% y/y to 20.9 million tons. However, in 2023 they decreased by 1.8% y/y to 20.6 million tons.
Colombia is the third supplier of coal to Europe with a share of 16.6%. In 2022, ships delivered 15.9 million tonnes to EU ports. Then deliveries increased by +89.2% y/y. But in 2023, demand from this direction decreased by 7.0% y/y to 14.8 million tons.
In fourth place was South Africa with a 9.1% share in European coal imports in 2023. In 2022, imports to the EU increased by 676.4% y/y to 16.0 million tonnes, but in 2023 . decreased by 49.5% y/y to 8.1 million tons. Indonesia provided only 5.4% of coal imports to Europe in 2023. Volumes from Indonesia to the EU increased by 1,148% y/y in 2022 to 5 .1 million tons, but decreased by 5.2% y/y in 2023 to 4.8 million tons.
Steel market
In 2023, global steel demand reached 1.814 billion tons. This information was provided by the updated short-term forecast of the World Steel Association (WSA). Worldsteel forecasts that in 2024, global demand for steel will increase by 1.9% y/y, to 1.849 billion tons. According to the World Steel Association, steel production in EU countries in 2022 decreased by 10.5% year on year – to 136.7 million tons. Overall, global steel production decreased by 4.3% y/y – to 1.83 billion tons.
Maximo Vedoya, CEO of Ternium and chairman of the Worldsteel economic committee, stated that “demand for steel is influenced by high inflation and high interest rates offered by banks,” reports Halina Yermołenko from GMK Center. According to Vedoya, activity in steel-consuming sectors has declined sharply since the second half of 2022, both in most industries and regions.
This trend continued in 2023, particularly affecting the EU and the US. The activity of the PRC economy has a significant impact on the global steel market. Several months ago, Worldsteel expected that the real estate market in China would stabilize in the second half of 2023. It was expected that the demand for steel in this country would increase by 2% y/y in 2023. However, the forecast for China for 2024 was still uncertain. And probably only when the Chinese New Year ends and the Year of the Dragon begins will we know more.
– We note that the Chinese economy is in the stage of structural transformation, which may increase volatility and uncertainty. Another uncertainty is related to regional conflicts and unrest. This could contribute to rising oil prices and further defragment the global economy, the association said in a statement.
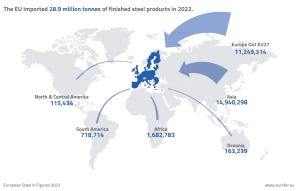
Steel European Union
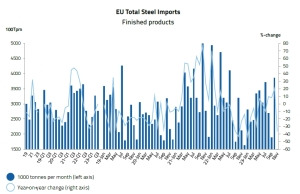
Last fall it was forecast that the demand for steel in EU countries and Great Britain in 2023, according to WSA forecasts, will decrease by 5.1% annually, and in 2024 it may increase by 5.8% y/y. In fact, imports of rolled steel during 11 months of last year decreased by 13% y/y
In the first 11 months of 2023, imports of finished products decreased by 13% y/y, including flat products – by 9% y/y and long products – by 25% y/y. In 2022, total imports of finished products decreased by 5% y/y. – informs Vadim Kolisnichenko in GMK Center, citing data from the Provincial Administrative Court.
– In the period from January to November 2023, the European Union (EU) reduced imports of steel (including semi-finished products) by 11% compared to the same period in 2022 – informs EUROFER in the “Economic and steel market outlook 2024” published in February -2025.” In 2022, overall steel imports also decreased by 7.3% y/y, while in 2021 they increased significantly by 32% y/y.
– In 2023, imports showed stable volatility, reflecting the fluctuations observed over the previous three years. After the outbreak of the Covid-19 epidemic, steel imports increased and showed some volatility in the second half of 2020. However, growth became much more pronounced in 2021, particularly in the second and third quarters, reaching all-time highs. These dynamics reflected favorable steel demand conditions until the end of 2021, while volatility continued in the fourth quarter of 2021 and throughout 2022, EUROFER reports.
The main countries supplying steel to the EU
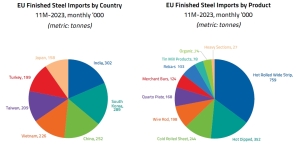
The main countries supplying steel to the EU in the period January-November 2023 were India (increase by 7% y/y), South Korea (increase by 6% y/y). Steel supplies from the PRC decreased by 13% y/y and from Turkey (-51% y/y). Meanwhile, steel deliveries by sea to the EU increased in Vietnam (38% y/y), Taiwan (12% y/y), and Japan (32% y/y). These countries accounted for over 58% of all deliveries by sea.
In the flat products segment, imports of all types of products decreased over the 11 months of last year. In particular, imports of cold-rolled and hot-rolled flat products decreased by 27% y/y and 22% y/y, respectively, while imports of coated products decreased by 24% y/y and organic steel by 30% y/y.
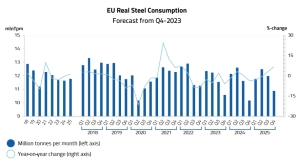
Among long products, positive growth by 2% y/y. only records recorded it. However, deliveries of reinforcing bars and wire rod decreased by 31% y/y and 26% y/y, respectively. EUROFER forecasts that in 2023, explicit steel consumption in the European Union will decrease by 6.3% compared to 2022, to 129 million tons. At the same time, in 2022 this number decreased by 6.5% y/y, and in 2024 it is expected to increase by 5.6% y/y.
During the last 11 months EU countries have produced 117.6 million tons of steel and still need it. Three main producers last year. these are the steel plants of the PRC (952.1 million t), India (128.2 million t) and Japan (80 million t). Lower imports of steel, and especially coal, allowed ports to catch their breath after the shortness of breath in 2022. Also Polish ports.
In 2023, 2,825 thousand coal and coke were transhipped in the terminals of the Port of Gdynia. t (in 2022 – 3,403 thousand t.). In Gdańsk there were 13.4 million tons in 2023 and 13.2 million tons in 2022. In the terminals of Szczecin and Świnoujście, 4,310.6 thousand tons were recorded in the statistics. tons of coal in the period January – December 2022 and 2,937.6 thousand t in 2023





 Article
Article  Article
Article