By Marek Grzybowski
The dynamically developing offshore wind energy industry will need installation ships. The jack-up market for offshore wind farms is being closely watched. New contracts are constantly being signed. This is despite disruptions in the OWE market, withdrawals from some contracts and changes in tenders for new installations.
Already two years ago, Rystad Energy predicted that the installation of offshore wind turbine heads with higher power than before may become a challenge for operators. The company’s analysts warned that in 2024, demand would exceed the availability of ships suitable for the needs of installation companies. The problem actually concerns not only the warheads, but also the foundations, monopiles and other parts necessary for the operation of MEW.
Rystad suggested that operators invest in new ships or modernize those already in operation. The lack of jack-ups with cranes with appropriate parameters on the market may result in bottlenecks in the process of building new wind farms in the middle of this decade.


High Demand for jack-ups and heavy lift vessels
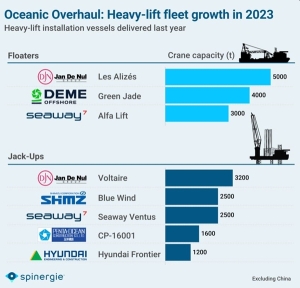
– A total of eight new heavy-duty jack-ups were delivered in 2023, which was a breakthrough year for the future of the maritime industry. This is the second highest number of deliveries recorded in one year, second only to the record from 2012, which saw ten deliveries, reports Spinergie.
Six operators took delivery of the new installation vessels. Among them, operator Jan De Nul, who directed the Les Alizés crane from China to Remontowa to the ship. It is one of the world’s largest offshore wind turbine installation vessels.
In March 2023, it was sent straight from the China Merchants Heavy Industries shipyard for reconstruction to the Gdańsk Remontowa Shipyard. We wrote about the ship here .
After the reconstruction, the “heavy lift vessel” could erect monopiles using a crane with a working load of 5,000. t. Can also be used to dismantle marine installations. Les Alizés was contracted to build the Gode Wind 3 and Borkum Riffgrund 3 wind farms in German waters. 107 foundations for wind towers and a transformer substation will be installed on German OWFs.
The Borkum Riffgrund 3 project, once commissioned, will be the largest offshore wind farm in Germany, and its commercial operation is scheduled to begin in 2025. Gode Wind 3 is being built simultaneously with Borkum Riffgrund 3 with a capacity of 900 MW. Both projects will be equipped with 11 MW Siemens Gamesa wind turbines. Borkum Riffgrund 3 is expected to come online next year.


Financial storms on wind farms
On this occasion, it should be mentioned that market turbulence caused Ørsted to sell 50% of shares in the Gode Wind 3 offshore wind farm with a capacity of 253 MW to funds managed by Glennmont Partners from Nuveen. The assignment agreement was signed in October last year. In addition, Glennmont also co-owns Ørsted’s Gode Wind 1 offshore wind farm.
The problems with investing in offshore wind and cautious investment in offshore vessels are explained by Spinergie analyst Yvan Gelbart: “In 2023, we did not have any new orders for vessels with heavy cranes. We understand that this is due to high interest rates and inflation , which makes signing a contract for a half-a-billion-dollar ship risky and impractical.”
DEME has included Green Jade with a 4,000 crane in its fleet. t in the middle of last year The operator already had several contracts. The unit was first directed to the installation of foundations for the 298 MW Zhong Neng project.
CSBC and DEME offshore jointly invested in the construction of the Green Jade installation vessel, with a total investment of TWD 2.1 billion (EUR 63.1 million). This is the second ship of this type to join the DEME fleet. The first Orion “crane” (worth approximately EUR 60 million) was introduced into the fleet in 2022.
Green Jade has dual-fuel engines and is Green Passport and Clean Design certified. Green Jade also has other innovations. The power plant has a waste heat recovery system that converts heat from exhaust gases and cooling water into electricity. The Huisman crane has a design that has a significant lifting height with a small minimum radius.
Time for jack-ups for offshore farms
Alfa Lift is a ship with a 3,000 m crane. i.e. for the transport of heavy elements belongs to Offshore Heavy Transport. It was put into operation in 2022. The ship has a transport and assembly deck with an area of over 10,000 m2. m². The ship can operate submerged to a depth of 15 m.
The hybrid system works based on a battery system. The electric-hybrid system is manufactured by Kongsberg. The ship can transport monopiles and other elements for the OWF. It can also be used to transport, install or remove overhead and underwater modules. More about the ship at GospodarkaMorska.pl
The Voltaire jack-up already operating in Germany is equipped with a 3.2 t crane, and the Blue Wind has a lifting capacity of 2.5 thousand. t. Japan Marine United (JMU) delivered at the end of January last year. Shimizu Corp. GustoMSC designed and equipped offshore wind turbine installation vessel (WTIV). Blue Wind is the largest WTIV in Japan to date. Jack up, Blue Wind will be used to install foundations and wind turbines.
Business plans for offshore wind farms to be revised
Both the price and availability of jack-up ships for the construction of wind farms are becoming a problem. Investors have been under increasing pressure from the economic slowdown since the beginning of 2023. Rystad Energy notes that this is not all.
Rising interest rates are putting pressure on the economic viability of new offshore wind projects. According to Rystad Energy, this causes many projects to become a financial burden on developers’ balance sheets – reports offshore-mag.com.
New projects require high initial investments to secure development rights and land, and then build and install large turbines whose average rotor diameter now exceeds 150 m.
In the UK, interest rates rose from 2022 to 5.25%. In 2023, the European Central Bank raised the interest rate by 4.25%, and at the beginning of September this year. back to 4.5%. The interest rate on main refinancing operations has remained unchanged since December last year. level of 4.5%. The central bank lending rate will be 4.75% and the deposit rate will be 4%. – These are the highest levels of interest rates in the euro zone since August 2001 – emphasizes “Bankier”.
Rystad analyst Shradha Sood said 2022 was a weak year for new activity in Europe as no financial investment decisions were made for commercial offshore wind farms. Difficulties in obtaining financing and rising prices of services were a big factor.
In July, Vattenfall suspended its project in the Norfolk Boreas in the southern UK North Sea. The suspension of works was justified by high interest rates and increased costs in the supply chain. The original contracted price for the execution and 37 SHP installations was GBP 35/MWh (USD 45.7/MWh) at 2012 prices. In 2023 it was approximately GBP 47.2/MWh (USD 57.51/MWh) at current prices .
– Political support and a review of the auction mechanism will be needed to revive investment in offshore wind, Sood suggested in mid-2022.
Slowdown in offshore windmills
It was estimated that as a result of market turmoil in supply chains, and especially price increases, the installed capacity of offshore wind energy increased by only 2% in 2023. This is the result of a delay in the implementation of offshore installations. According to WindEurope, in 2023, new offshore wind farms with a total capacity of 3 GW were built in the EU. For comparison, 14 GW was installed on land.
– Wind energy – both onshore and offshore, which was previously on a strong growth path – has encountered obstacles that have hindered its development – says Vegard Wiik Vollset, vice president and head of renewable energy research in the EMEA region at Rystad Energy – quotes offshore -mag.com..
As expected, the European offshore wind sector recorded last year a modest 2% annual install growth. Offshore wind energy shows a strong growth trend, but the recent wave of delays in the implementation of key projects has highlighted the sensitivity of the market – Rystad Energy experts point out.
At the end of last year the UK and Denmark were predicted to miss their 2030 offshore wind targets.
OWE progress in Europe
The UK is expected to achieve a maximum of 46.8GW of offshore wind capacity by 2030. This means the government’s target of 50GW will not be met. Similarly, Denmark is expected to install just over 10 GW offshore, compared to 12 GW planned in 2030.
At the end of 2021, the global fleet of foundation installation vessels consisted of 17 vessels. In 2022, the fleet increased by 5 units, and in 2023 by 8 installation ships. Each worth approximately EUR 520 to EUR 620 million. It’s still not enough. because Rystad claims that “despite the obstacles it encounters, the offshore wind industry continues to persevere, demonstrating resilience and long-term prospects.”
We are making progress in Europe, as France has recently put into operation the first offshore wind farms in the Saint-Brieuc and Fecamp water areas. The world’s largest floating offshore wind farm, owned by Equinor Hywind Tampen, with a capacity of 88 MW, began operation off the coast of Norway. This was widely discussed during the Floating Wind Days in Norway last May. Let us emphasize, a conference that gathered all major players interested in MEW.
But getting offshore wind back on a growth path will require significant changes in project development and permitting processes, Rystad experts say.
It is necessary to improve the supply chain and undertake new investments. The beneficiary of this activity is, among others: West Pomeranian Voivodeship and Pomeranian Voivodeship. A plant producing installations for OWE is being built on the premises of the former Gdańsk Shipyard and in the Pomeranian Special Economic Zone. The investor is ARP and its partner from Spain.
King Frederick X of Denmark laid the foundation stone for the construction of a gondola factory for offshore wind farms by the Danish company Vestas in Szczecin on February 2 this year. The plant is to be built in Ostrów Brdowski in the former ST3 Offshore hall complex. In Poland, construction of a factory for the production of nacelles for offshore wind turbines has begun in earnest.



Wind Offshore business requires investment
Wind Offshore business also requires continuous investment in research and development. Here, offshore projects include the activities of the Ship Technology Center, the Polish Register of Shipping, and the Offshore Center of the Maritime University of Gdynia. An important role is played by higher education and MBA studies conducted by the Maritime University and the Maritime University of Technology, the Gdańsk University of Technology and the University of Gdańsk.
An important task was entrusted to the Maritime Wind Energy Center of the University of Gdańsk and the Maritime Economy Research Center of the University of Gdańsk. Vocational training has been provided by the Maritime School in Gdynia at Polska Street for over 20 years.
Investors must verify their business plans, which must take into account the rising prices of supply chain elements, the increase in the prices of components for OWE and the costs of services and logistics. But the biggest challenge will likely be the availability of installation vessels equipped with appropriate cranes.
Acquiring staff with appropriate qualifications, predispositions and ready to work in dangerous conditions will also be a significant challenge. Accelerating investments in OWE in the North Sea and in the coastal zones of European Union countries may pose a threat to the development of OWE in the Baltic Sea and Poland.
Wind farm components and staff produced in Poland may be sucked out of our market. Therefore, the Polish OWE may be threatened by the improving economic situation on the markets of Great Britain, Denmark, Norway and Germany, as well as the developing markets of OWE in the Atlantic and the Mediterranean Sea.